Human Rights in Sudan: Background, Violations & Challenges
The current human rights situation in Sudan is a complex phenomenon woven from historical legacies, political turmoil, and socio-economic struggles. This article seeks to dissect the layers of challenges faced by the Sudanese population, delving into historical contexts, contemporary issues, and potential pathways toward a more sustainable future.
Related Post: What’s happening in Sudan?
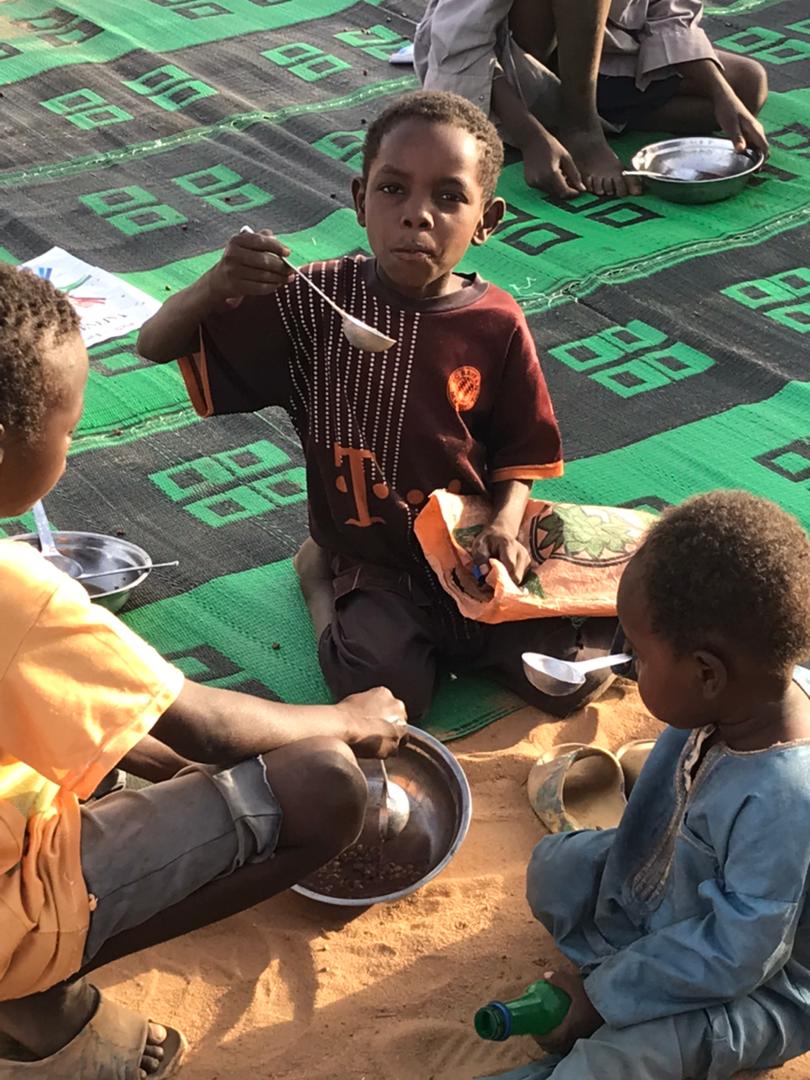


Human Rights in Sudan:
Historical Context
Understanding the contemporary human rights landscape in Sudan requires a journey through its rich history. The impact of colonialism, subsequent post-colonial developments, and the intricacies of political transitions have left an indelible mark on the nation, shaping the dynamics of human rights challenges.
Civil and Political Rights
Within the realm of civil and political rights, Sudan grapples with a myriad of challenges. The freedom of expression, political participation, and the rule of law often find themselves compromised, leading to a stifled democratic environment. Notable cases and incidents, such as the suppression of dissent or limitations on political freedoms, warrant closer scrutiny to comprehend their implications for the broader population.
Economic and Social Rights
The economic and social dimensions of human rights are equally critical in Sudan. High levels of poverty leading to food crises, limited access to education, and healthcare disparities persist, demanding a comprehensive analysis of economic policies and their implications on human rights. Evaluating the impact of economic decisions on the everyday lives of Sudanese citizens is imperative for understanding the root causes of these challenges.
Women’s Rights
Despite notable strides towards gender equality, women’s rights in Sudan encounter persistent obstacles. Gender-based violence, discriminatory practices, and the effectiveness of existing legal frameworks demand careful consideration. Exploring the role of women in societal transformation becomes a focal point in envisioning a more inclusive future.
Ethnic and Religious Minorities
Ethnic and religious minorities face unique challenges in Sudan, including discrimination, displacement, and efforts for inclusivity. Delving into the historical and cultural factors contributing to these challenges sheds light on the intricacies of identity politics in the nation. Understanding the nuanced dynamics of these communities is crucial for fostering a climate of tolerance and diversity.
Related Post: Is Sudan Safe to Travel


Human Rights Violations in Sudan
Sudan has experienced significant human rights violations, marked by a complex history of political unrest and armed conflicts. Some notable instances of human rights abuses include:
1. Civil Conflicts:
The protracted civil conflicts in Sudan, particularly the Second Sudanese Civil War (1983-2005), resulted in widespread human rights violations, including displacement, atrocities against civilians, and the recruitment of child soldiers.
2. Darfur Conflict:
The Darfur conflict, beginning in the early 2000s, led to severe human rights abuses, including mass killings, displacement of populations, sexual violence, and alleged war crimes. The International Criminal Court issued warrants for the arrest of Sudanese officials accused of orchestrating these atrocities.
3. Restrictions on Freedom of Expression:
The Sudanese government, both past and present, has been criticized for restricting freedom of expression. Journalists, activists, and dissenting voices have faced censorship, harassment, and imprisonment.
4. Religious Persecution:
Sudan has a history of religious persecution, with incidents targeting minority religious groups. The enforcement of strict Islamic laws at various points in history has resulted in discrimination against non-Muslim communities.
5. Gender-Based Violence:
Gender-based violence remains a concern in Sudan, with instances of domestic violence, early and forced marriages, and the lack of legal protection for victims.
6. Use of Excessive Force:
Protests against the government have been met with the use of excessive force by security forces. The violent suppression of demonstrations has led to casualties and injuries among protesters.
7. Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs):
Ongoing conflicts and violence have forced a significant number of Sudanese citizens into internal displacement. IDPs face challenges in accessing basic services, leading to humanitarian concerns.
Sudan Humanitarian Crisis
Ongoing humanitarian crises compound human rights challenges, with displacement, hunger, lack of water, and health crises affecting vulnerable populations. The article explores the impact on the population, the response of humanitarian organizations, and the effectiveness of international aid efforts in mitigating the suffering of the Sudanese people.
International Response
The role of the international community in addressing Sudan’s human rights violations is a nuanced aspect. Sanctions, aid, and diplomatic efforts require scrutiny to assess their impact and effectiveness in fostering positive change. The article delves into the complexities of international interventions, analyzing their implications on the ground and the challenges faced in implementing them. SAPA is actively working to help the people of Sudan in their time of need. To help them contribute to the Sudan humanitarian crisis, Donate Now.
Government Initiatives
Exploring government initiatives aimed at improving human rights reveals a complex landscape of policies and reforms. Evaluating their effectiveness, particularly in addressing root causes and achieving sustainable change, is essential. This section also discusses the challenges faced by the government in implementing these initiatives and the need for a collaborative approach involving all stakeholders.
Challenges to the Implementation of Human Rights
The implementation of human rights measures faces hurdles on various fronts, including political, cultural, and economic obstacles. Identifying these challenges and proposing viable solutions forms a crucial aspect of navigating toward meaningful change. The article explores the interconnected nature of these challenges and how addressing them collectively can pave the way for a more rights-respecting society.
Local Activism & Sudan Human Rights
The role of local activists and organizations in advocating for human rights is indispensable. In-depth stories of specific activists and their impact showcase the resilience and determination of Sudanese individuals working towards positive change. By highlighting these stories, the article aims to inspire others and underscore the importance of local initiatives in driving change.
Media Influence
The media plays a pivotal role in shaping human rights awareness in Sudan. Analyzing the impact of journalism, social media, and communication technologies reveals instances where media has been a powerful force in highlighting and addressing human rights issues. This section discusses the responsibilities of the media, the challenges they face, and the potential for constructive influence in shaping public opinion and fostering accountability.
Education and Awareness
Promoting education and awareness emerges as a fundamental strategy for advancing human rights. Initiatives and programs focused on educating the public, coupled with the role of educational institutions, NGOs, and community outreach, contribute to fostering a culture of respect for human rights. By examining the role of education and awareness, the article underscores the importance of empowering individuals with knowledge to create positive societal change.
Future Outlook
Envisioning the future of human rights in Sudan requires considering emerging political, social, and economic factors. The article provides insights into potential trajectories and emphasizes the need for proactive measures to ensure positive outcomes. By considering the evolving landscape, the article aims to contribute to a constructive dialogue on shaping a future where human rights are upheld and protected.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate web of human rights challenges in Sudan, including access to essential resources like water wells, underscores the need for collective and sustained efforts. This article serves as a call to action, urging stakeholders at local, national, and international levels to work collaboratively for a brighter and more equitable future for all Sudanese citizens. The interconnectedness of various human rights issues, coupled with the critical importance of initiatives like Sudan online donations, Sudan children donations, Sudan relief fund, and Water for South Sudan, emphasizes the need for comprehensive solutions. These solutions should address the root causes of human rights challenges while promoting a culture of respect for human rights.
Furthermore, considering Sudan’s socio-economic context, understanding concepts like Zakat Nisab and Zakat al Fitr becomes crucial in fostering a holistic approach to humanitarian efforts and sustainable development in the region.
FAQs
1. What historical factors contribute to the human rights situation in Sudan?
Sudan’s layered human rights challenges arise from colonial legacies and post-independence conflicts between the Arab-Muslim north and the African-Christian or animist south, shaping current ethnic and political strife in one of the poorest countries in the world.
2. What restrictions on civil and political rights exist in Sudan?
Sudan continues to experience severe limits on freedom of expression and political participation, with state-led censorship and repression being common in recent Sudan human rights reports.
3. How severe are economic and social rights challenges in Sudan?
Over 30 million people in Sudan require urgent humanitarian assistance due to widespread poverty, food insecurity, limited healthcare, and poor educational access.
4. What challenges do women face regarding rights in Sudan?
Despite some legal progress, women’s rights in Sudan remain constrained by ongoing gender-based violence; the UN documented over 120 cases of sexual violence from recent conflicts.
5. How are ethnic and religious minorities affected by human rights violations?
Minority groups in regions like Darfur endure displacement, discrimination, and violence, exacerbating ethnic tensions and humanitarian crises.
6. What has been the scale of displacement and civilian impact since the latest conflict escalation?
Since April 2023, over 12 million people have been displaced, including 11.6 million internally displaced, making Sudan host to the world’s largest internal displacement crisis.
7. What is the international community’s role in addressing Sudan’s human rights crisis?
The UN, African Union, and other actors have deployed peacekeeping missions and implemented sanctions, but face challenges like limited access and non-cooperation from armed groups.
8. What role do activists and media play in Sudan’s human rights landscape?
Local activists, especially women and youth, drive reform efforts and raise awareness, while the media expose abuses, fostering public accountability and engagement.
9. How does education influence human rights awareness in Sudan?
Educational outreach advances public understanding of rights, empowering citizens to advocate for justice and reform critical to societal change.
10. How can donations to SAPA support human rights and humanitarian needs in Sudan?
Donations to SAPA’s programs, including water wells, relief funds, and support for children and women, provide crucial health, nutrition, and protection services for millions affected by the ongoing Sudan Crisis.