Water Crisis in Sudan: Impact & Challenges [4 Causes]
South Sudan, a nation grappling with the aftermath of decades of conflict, is facing an acute water crisis that demands urgent attention. The scarcity of clean and accessible water poses significant challenges to the health, well-being, and overall development of its population. In this article, we delve into the complexities of the South Sudan water crisis, exploring its root causes, the impact on communities, ongoing efforts to address the issue, and the imperative for sustained global support.
Understanding the Water Crisis in South Sudan
South Sudan gained independence in 2011, following years of civil war with Sudan. Despite this newfound sovereignty, the nation has been plagued by internal conflicts and political instability, hindering the development of basic infrastructure, including water supply systems.
The lack of a robust and accessible water supply system poses a direct threat to the well-being of South Sudanese communities. Limited access to clean water not only jeopardizes the health of the population but also impedes progress in areas such as education and economic development. Communities are forced to rely on inadequate and unsafe water sources, leading to waterborne diseases and perpetuating a cycle of poverty.
Addressing the water crisis in Sudan requires a comprehensive approach that goes beyond immediate relief efforts. Sustainable solutions involve the establishment of infrastructure that can withstand the challenges posed by internal conflicts and political instability. International support and collaborative efforts are crucial in providing technical expertise, financial resources, and long-term strategies to ensure a stable and reliable water supply for the people of Sudan.
Root Causes of the Sudan Water Crisis:
1. Infrastructure Challenges: The lack of robust infrastructure for water supply and sanitation is a fundamental contributor to the crisis. Many communities lack access to safe and clean water sources.
2. Climate Variability: South Sudan is vulnerable to climate variability, experiencing both droughts and floods. These extreme weather events disrupt water sources and exacerbate the challenges faced by communities.
3. Population Displacement: Ongoing conflicts have led to widespread internal displacement, with many families forced to live in temporary shelters. The concentration of displaced populations puts immense pressure on available water resources.
4. Economic Constraints: Limited financial resources have impeded the government’s ability to invest in water infrastructure projects. The economic challenges faced by Sudan have hindered progress in addressing the water crisis.


>> Recommended Read: Top 10 Poorest Countries in the World
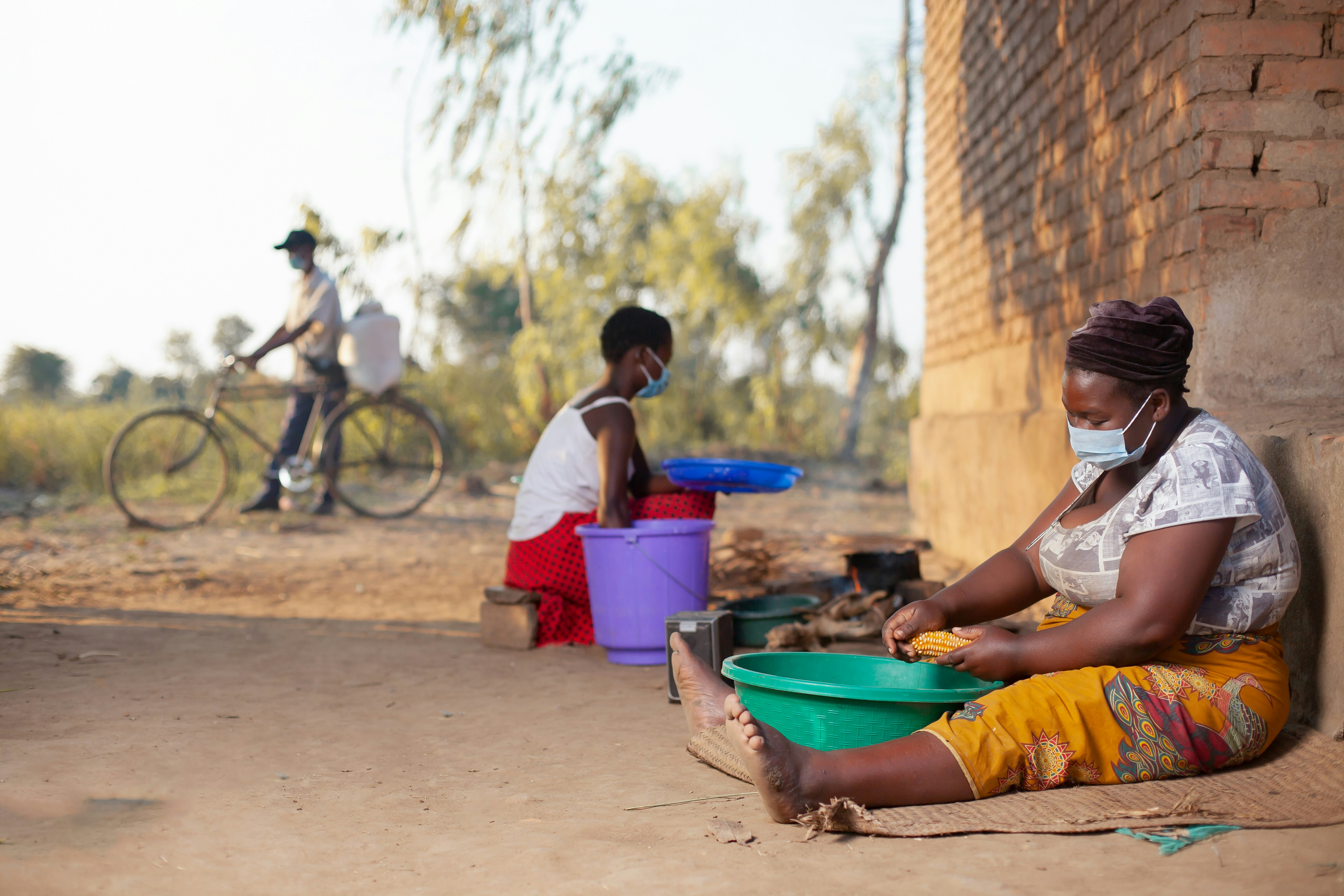
Impact of Water Crisis on Sudanese Communities:
1. Health Ramifications
The scarcity of clean water has severe implications for public health. Waterborne diseases, such as cholera and typhoid, are rampant due to the consumption of contaminated water. Lack of access to sanitation facilities further compounds these health challenges.
2. Women and Children Bearing the Brunt
In many communities, the responsibility for fetching water falls predominantly on women and children. The arduous task of walking long distances to collect water takes a toll on their well-being and hinders their educational and economic opportunities.
3. Agricultural Dilemma
For a nation heavily dependent on agriculture, the water crisis has dire consequences for the Food Crisis. Insufficient water for irrigation affects crop yields, perpetuating a cycle of food scarcity and economic hardship.
>> Related Post: Best Sudanese charities to donate to
Ongoing Efforts to Address the Crisis:
Community-Led Solutions: Local communities, with support from non-governmental organizations (NGOs), are implementing water management and conservation strategies. This includes the construction of rainwater harvesting systems and the rehabilitation of existing water sources, including Water Wells.
Humanitarian Aid: International organizations and humanitarian agencies are actively involved in providing emergency relief. This includes the distribution of water purification tablets, the construction of boreholes, and hygiene education programs.
Government Policies: The South Sudanese government, despite economic challenges, has recognized the urgency of the water crisis. National policies are being formulated to prioritize water infrastructure development and improve access for marginalized communities.
Amid the crisis, SAPA’s Water for Sudan has provided hands-on donations and support to the people of Sudan. In order to become part of the solution, Sudan Sudan donations online to help the locals in their time of need.
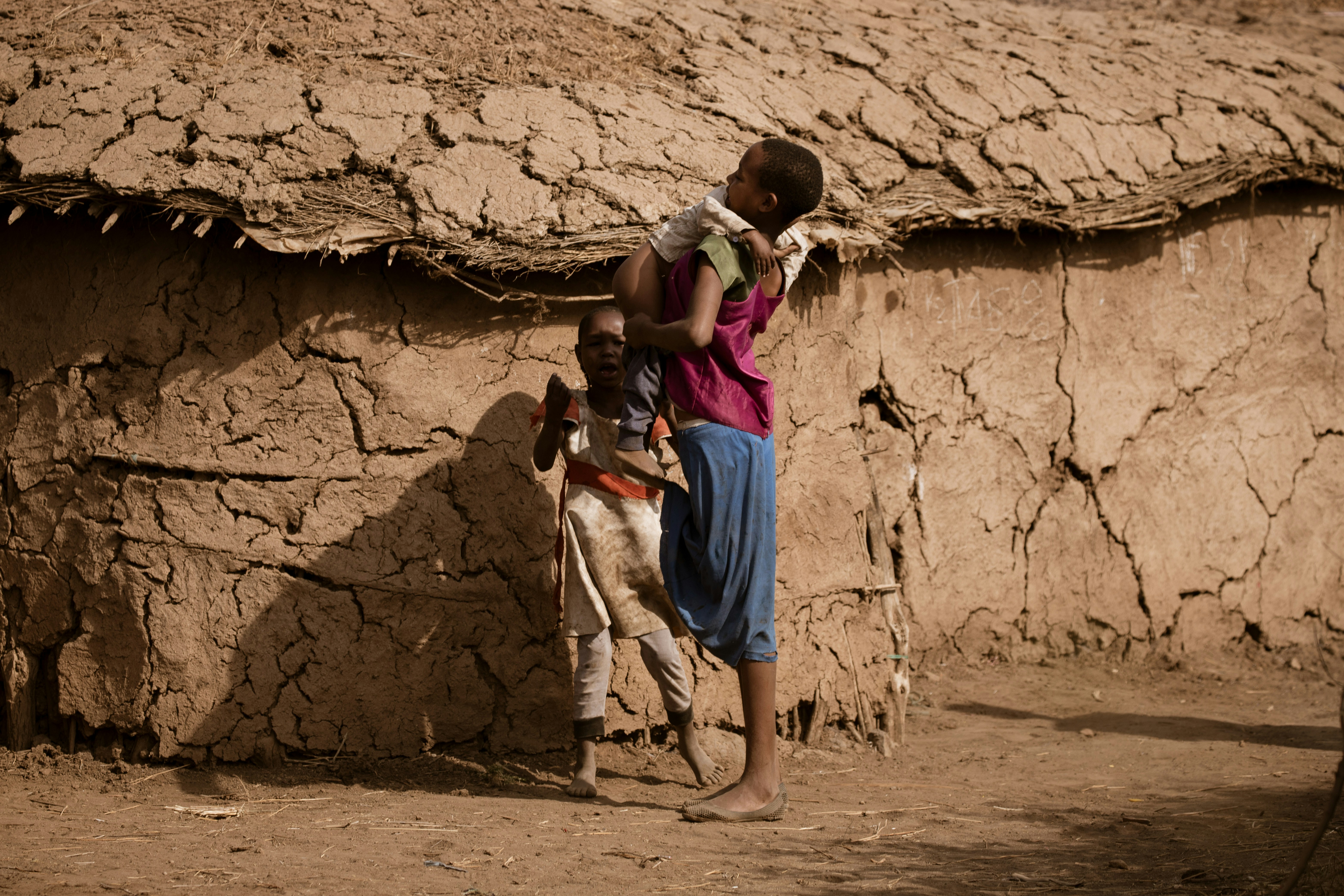


The Imperative for Sustained Global Support
Investing in Infrastructure
One of the primary solutions to the South Sudan water crisis lies in substantial investments in water infrastructure. Building resilient and sustainable water supply systems, including wells, boreholes, and water treatment plants, is crucial for ensuring access to clean water.
Climate Resilience Measures
Given Sudan’s climate change issue, implementing climate-resilient water management practices is essential. This involves incorporating climate-smart technologies, such as rainwater harvesting systems, to mitigate the impact of extreme weather events on water sources.
Capacity Building and Education
Empowering local communities with the knowledge and skills to manage water resources effectively is integral to addressing the crisis. Education programs on water conservation, sanitation, and hygiene practices contribute to long-term sustainability.
Collaborative International Efforts
The water crisis is a global challenge that necessitates collaborative efforts. International partnerships, financial aid, and technical support are crucial for implementing large-scale water infrastructure projects and supporting grassroots initiatives.
MAKE A DONATION
The recent floods in Sudan have unleashed a severe public health crisis, with waterborne diseases, especially cholera, surging at an alarming rate. Over 11,000 cholera cases have been reported since June 2023, with the situation worsening as 556 new cases and 27 deaths were recorded recently. The hardest-hit areas—Khartoum, Gezira, Kordofan, and Darfur—are struggling to cope with the outbreak as contaminated water continues to spread the disease. Immediate action is needed to provide clean water and medical supplies to prevent further loss of life. Your support is crucial in combating this escalating health emergency.
Conclusion
The water crisis in Sudan is a multifaceted challenge that demands immediate attention and sustained efforts. The impact on public health, agriculture, and overall socio-economic development underscores the urgency of finding comprehensive solutions. As local communities, governments, and international organizations work together, there is hope for a future where every South Sudanese citizen can access clean and safe water. The global community must continue to prioritize and support initiatives that address the root causes of the crisis, fostering a resilient and water-secure Sudan.
FAQs
1. How did South Sudan’s civil war and political instability lead to its water crisis?
The prolonged conflict disrupted infrastructure development, leaving water supply systems underdeveloped and unreliable, worsening access for communities.
2. What are the main factors causing the water crisis in Sudan today?
Key drivers include damaged infrastructure, unpredictable climate patterns, displacement of populations, and economic limitations that hinder water resource management and service delivery.
3. In what ways does the water crisis threaten public health in Sudan?
Limited access to safe water results in widespread waterborne illnesses such as cholera and typhoid, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality rates in vulnerable populations.
4. Which innovative water technologies are transforming rural water access in South Sudan?
Advanced solutions like solar-powered pumps and rainwater harvesting systems are vital, especially as climate impacts are projected to cause a significant 30% reduction in water availability due to increased droughts and evaporation rates, aligning with strategies discussed in Sudan climate challenges.
5. How do refugee settlements impact South Sudan’s water resource management?
South Sudan hosts over 544,000 refugees mainly from Sudan, increasing pressure on water infrastructure and complicating equitable distribution, as highlighted in South Sudan water crisis.
6. What complementary health measures support water supply improvements to reduce waterborne diseases?
Integrated water, sanitation, and hygiene interventions can reduce disease incidence by up to 30%, supported by initiatives like Water Wells projects.
7. How can empowering local communities ensure sustainable water system management in South Sudan?
Training residents in maintenance, monitoring, and conservation fosters ownership and resilience, which is critical given the area’s instability and highlighted by successful community-led models.
8. What is the impact of international partnerships on improving South Sudan’s water infrastructure?
Global collaborations provide essential funding, technical support, and policy guidance, enabling large-scale projects and emergency response efforts, as exemplified by initiatives such as Water for Sudan.
9. How does climate variability affect water availability and quality in South Sudan?
Shifts in rainfall and extreme events like droughts and floods damage water sources and increase scarcity, making climate resilience a crucial component in water planning, supported by insights from flood response efforts.
10. What economic barriers prevent South Sudan from resolving its water crisis effectively?
Low government revenue and competing priorities limit infrastructure investment and upkeep, emphasizing the importance of international financial aid and innovative funding for post-conflict recovery.
11. How does water collection burden disproportionately impact women and children in South Sudan?
The time and effort required to reduce women’s economic participation and children’s schooling, perpetuating poverty and gender inequality, highlighting the need for targeted measures to alleviate these hardships.





Comments (2)
claire
can you share if anyone has tried to solve it and if they did what did they do
brycen
i think they did solve it