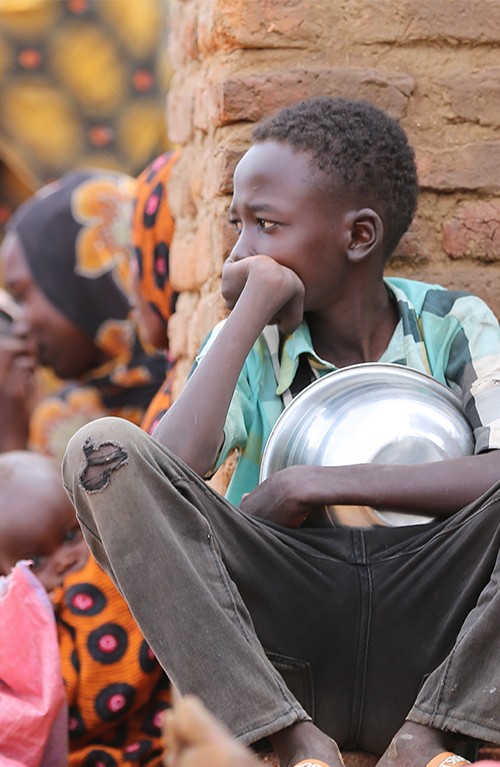Hunger in Africa: Addressing Famine, Starvation, and Food Insecurity
Hunger in Africa is a heartbreaking reality that affects millions of people. The images of malnourished children and desperate families are a stark reminder of the ongoing food crisis. Despite the continent’s rich resources and potential, many African nations face severe food insecurity, leading to widespread famine and starvation. This blog explores the causes and effects of hunger in Africa, highlights the incredible work of the Sudanese American Physicians Association (SAPA) in alleviating this crisis, and shows how you can contribute to making a difference.
Causes of African Food Crisis in 2026:
‘’According to the UN, 46 million people in Africa experienced hunger in the aftermath of the Covid-19 pandemic – that’s the highest share of any continent in the world’’ (British RedCross)
1. Climate Change
Climate change has wreaked havoc on Africa’s agricultural systems. Prolonged droughts, unpredictable rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events have devastated crops and livestock. Farmers rely heavily on consistent weather patterns and are often left with nothing after a lousy season. Entire communities face food shortages, and the cycle of poverty deepens as the land becomes less fertile and productive.
2. Conflict and Political Instability
Wars and political unrest are rampant in many parts of Africa. These conflicts disrupt food production and distribution, displacing millions of people and preventing them from accessing food. The constant threat of violence makes it impossible for families to farm their land, leading to abandoned fields and lost harvests. The humanitarian crisis is exacerbated by a lack of access to food and necessities.
3. Poverty
Poverty is both a cause and a consequence of hunger. High levels of poverty mean that many families cannot afford nutritious food, leading to chronic malnutrition. Without proper nutrition, individuals cannot work effectively, perpetuating the cycle of poverty and hunger. The lack of economic opportunities and social safety nets leaves millions vulnerable to food insecurity.
4. Poor Agricultural Practices
Many African farmers lack access to modern farming techniques and inputs, limiting their crop yields and food availability. Traditional farming methods, while sustainable in the past, are often insufficient to meet the demands of growing populations. Without proper education and resources, farmers cannot adopt more efficient practices that could help them produce more food.
5. Economic Factors
Rising food prices and economic downturns make it increasingly difficult for families to purchase food. Inflation, unemployment, and economic instability exacerbate food insecurity, leaving many without the means to feed their families. The global economic landscape also impacts Africa, with trade imbalances and foreign debt affecting local economies.
Interested in Making a Donation? Learn about the Best Charities in Africa
Effects of Food Insecurity & Hunger in Africa in 2026:
1. Malnutrition and Health Issues
Malnutrition weakens immune systems, making individuals more susceptible to diseases. Children suffer the most, with malnutrition leading to stunted growth, cognitive impairments, and higher mortality rates. Pregnant women and the elderly are also at high risk, facing severe health complications due to a lack of proper nutrition.
2. Education
Hungry children need help to concentrate in school, leading to poor academic performance and high dropout rates. Without education, the next generation is left ill-equipped to break the cycle of poverty and hunger. The long-term effects on human capital are profound, with entire communities losing out on the potential of their young minds.
3. Economic Impact
Hunger reduces productivity and economic growth as malnourished individuals are less able to work and contribute to their communities. The workforce is weakened, and the economic potential of nations is stifled. The economic burden of treating hunger-related illnesses further strains already limited resources.
4. Social Unrest
Food shortages can lead to social instability, conflicts, and migrations. Desperation drives people to flee their homes in search of food, leading to overcrowded refugee camps and strained resources in host communities. The competition for scarce resources often sparks violence and unrest, further complicating the humanitarian crisis.
How SAPA is Helping Deal with Hunger in Africa
The Sudanese American Physicians Association (SAPA) is playing a crucial role in combating hunger in Africa (Sudan). SAPA’s dedicated team of volunteers and medical professionals works tirelessly to provide relief to those affected by hunger and malnutrition. Our efforts are a beacon of hope in the midst of despair.
- Medical Missions
SAPA organizes medical missions to remote and underserved areas, providing essential healthcare services, nutritional support, and education on healthy practices. These missions not only address immediate health needs but also offer long-term solutions by educating communities about nutrition and hygiene.
- Food Distribution
SAPA collaborates with local partners to distribute food and nutritional supplements to communities in need as part of their hunger relief program. By ensuring that families have access to essential nutrients, SAPA helps prevent malnutrition and its devastating effects. Their efforts often make the difference between life and death for many individuals.
- Child Nutrition Programs
SAPA focuses on improving child nutrition by providing meals in schools, supporting maternal and child health programs, and educating communities on proper nutrition. These programs ensure that children receive the nourishment they need to grow and thrive, laying the foundation for a healthier future.
- Sustainable Solutions
SAPA promotes sustainable agricultural practices and supports local farmers in increasing food production and improving food security in the long term. By providing training and resources, SAPA empowers farmers to adopt more efficient and productive farming methods, ensuring a stable food supply for their communities.
>> Related Post: Best Children’s Charities to Donate to
Contributions You Can Make to Alleviate Starvation in Africa:
The fight against hunger in Africa requires collective effort. Every contribution, no matter how small, can make a significant difference in the lives of those affected by hunger.
1. Donate
Financial contributions to organizations like SAPA can provide immediate relief and support long-term solutions to hunger. Your donations help fund medical missions, food distribution, and child nutrition programs, directly impacting those in need.
2. Volunteer
Become a volunteer and offer your time and skills to support local and international hunger relief efforts. Whether you can volunteer locally or travel to affected areas, your efforts can bring hope and help to those suffering from hunger.
3. Raise Awareness
Use your voice to advocate for policies and initiatives that address the root causes of hunger and promote food security. Sharing information and stories about the hunger crisis can inspire others to take action and support the cause.
4. Educate Others
Share information about the hunger crisis in Africa and encourage others to get involved in making a difference. Education is a powerful tool for change, and spreading awareness can lead to collective action and lasting solutions.
Conclusion
The hunger crisis in Africa is a complex and heart-wrenching issue that requires urgent action. While the challenges are immense, organizations like SAPA are making significant strides in alleviating hunger and improving lives. By supporting these efforts, whether through donations, volunteering, or raising awareness, we can all play a part in ending hunger in Africa. Together, we can bring hope and nourishment to those who need it most.
FAQs
1. What are the main causes of poverty in Africa?
Economic instability, conflict, health crises, lack of education, climate change, and poor governance drive poverty in Africa. These systemic issues are elaborated in the analysis of poverty causes in Africa, affecting millions across the continent.
2. Which African country is the poorest in 2025?
Burundi is the poorest country, with a GDP per capita of $214. It faces severe economic challenges, including political instability and an inflation rate that surged to 39% in early 2025, detailed in the Burundi economic overview.
3. What are the top ten poorest African countries by GDP per capita in 2026?
The list includes Burundi, Madagascar, Malawi, Central African Republic, Sierra Leone, Sudan, South Sudan, Mozambique, Somalia, and Democratic Republic of Congo. Details are found on the top 10 poorest African nations blog post.
4. How does conflict exacerbate poverty in African countries?
Conflicts cause displacement, economic disruption, and destruction of infrastructure, leading to long-term poverty cycles.
5. What healthcare challenges contribute to poverty?
Diseases such as malaria, HIV/AIDS, and tuberculosis reduce workforce productivity and strain healthcare systems. Healthcare initiatives targeting these issues support affected populations.
6. How does lack of education perpetuate poverty?
Limited access to education restricts economic opportunities, sustaining generational poverty. Programs like Help Kids in Africa help break this cycle through scholarships and infrastructure.
7. What role does climate change play in impoverishment?
Climate change causes droughts, floods, and food insecurity, affecting agriculture-dependent communities. Humanitarian aid efforts such as the North Africa Food Relief address these crises.
8. How do poor governance and corruption affect poverty?
Corruption siphons funds from essential public services and undermines trust, obstructing development. Transparency and accountability are promoted through corporate philanthropy programs.
9. What healthcare services help alleviate poverty?
Medical interventions, including surgeries, health education, and programs like Sight in Sudan treat preventable blindness and improve health outcomes.
10. How do education and community projects foster sustainable development?
Initiatives in clean water, sanitation, and education, such as Water for Sudan, empower communities. Success stories like Qais’s recovery and Amona’s journey illustrate impact.